redis基础
Redis 基础知识
Redis is a very fast non-relational database that stores a mapping of keys to five different types of values.
Redis Data structure
STRINGs, LISTs, SETs, HASHes, and ZSETs.
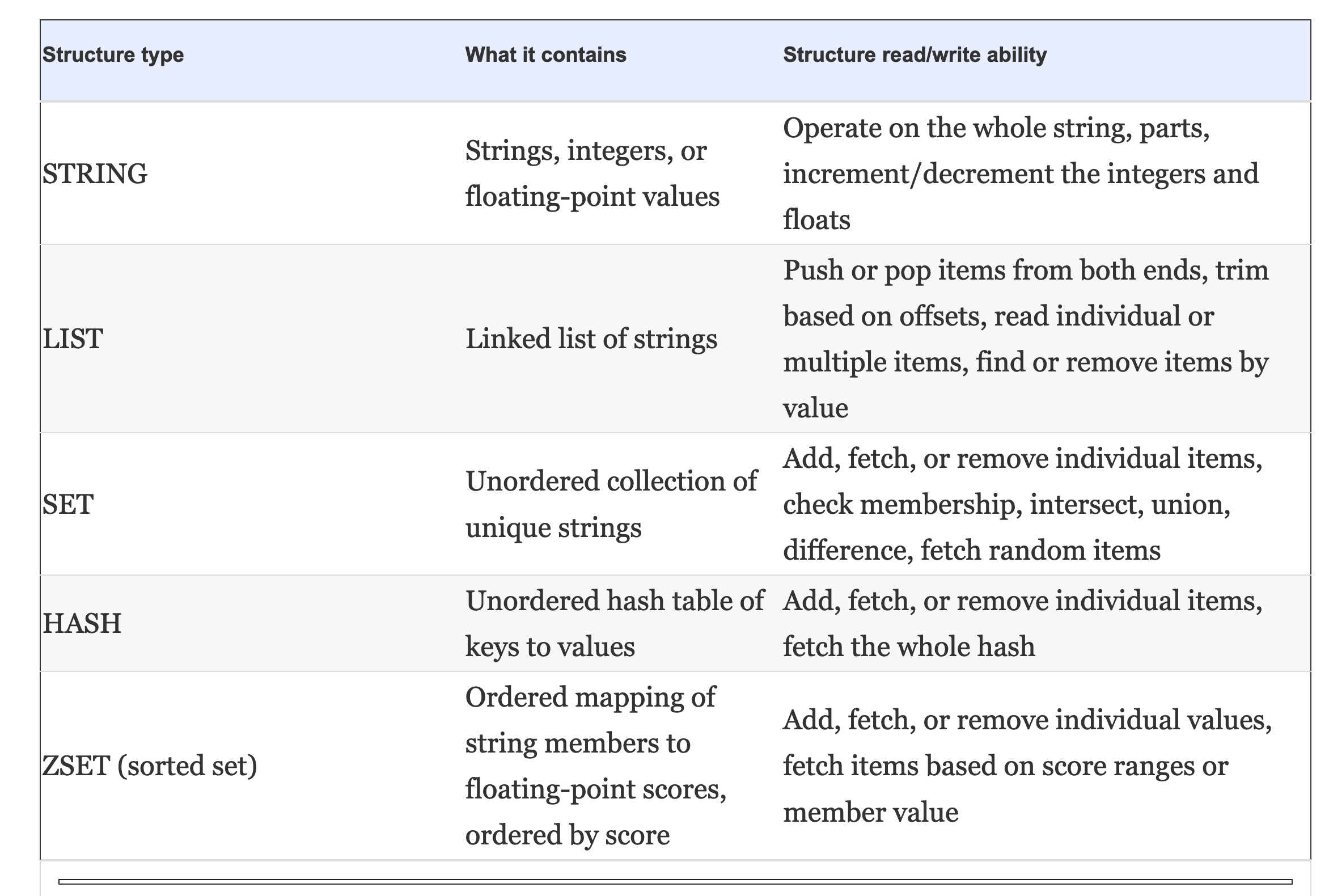
1. Strings
| Command | What it does |
|---|---|
| GET | Fetches the data stored at the given key |
| SET | Sets the value stored at the given key |
| DEL | Deletes the value stored at the given key (works for all types) |
2. LIST
| Command | What it does |
|---|---|
| RPUSH | Pushes the value onto the right end of the list |
| LRANGE | Fetches a range of values from the list |
| LINDEX | Fetches an item at a given position in the list |
| LPOP | Pops the value from the left end of the list and returns it |
3. SETS
| Command | What it does |
|---|---|
| SADD | Adds the item to the set |
| SMEMBERS | Returns the entire set of items |
| SISMEMBER | Checks if an item is in the set |
| SREM | Removes the item from the set, if it exists |
4. HASH
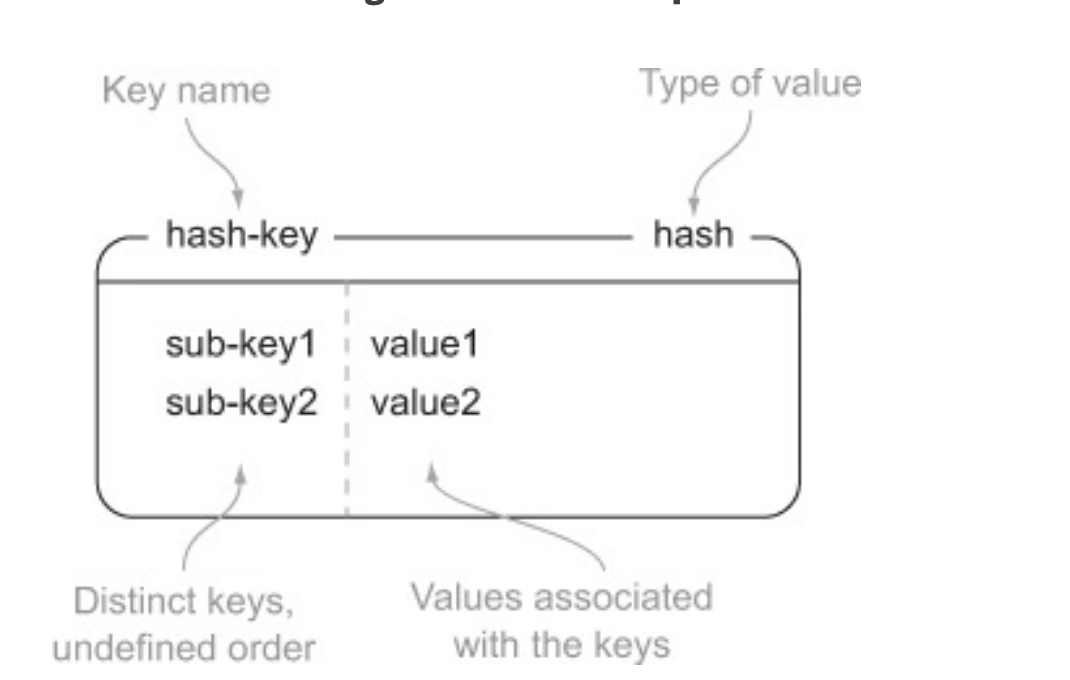
| Command | What it does |
|---|---|
| HSET | Stores the value at the key in the hash |
| HGET | Fetches the value at the given hash key |
| HGETALL | Fetches the entire hash |
| HDEL | Removes a key from the hash, if it exists |
5. ZSETS
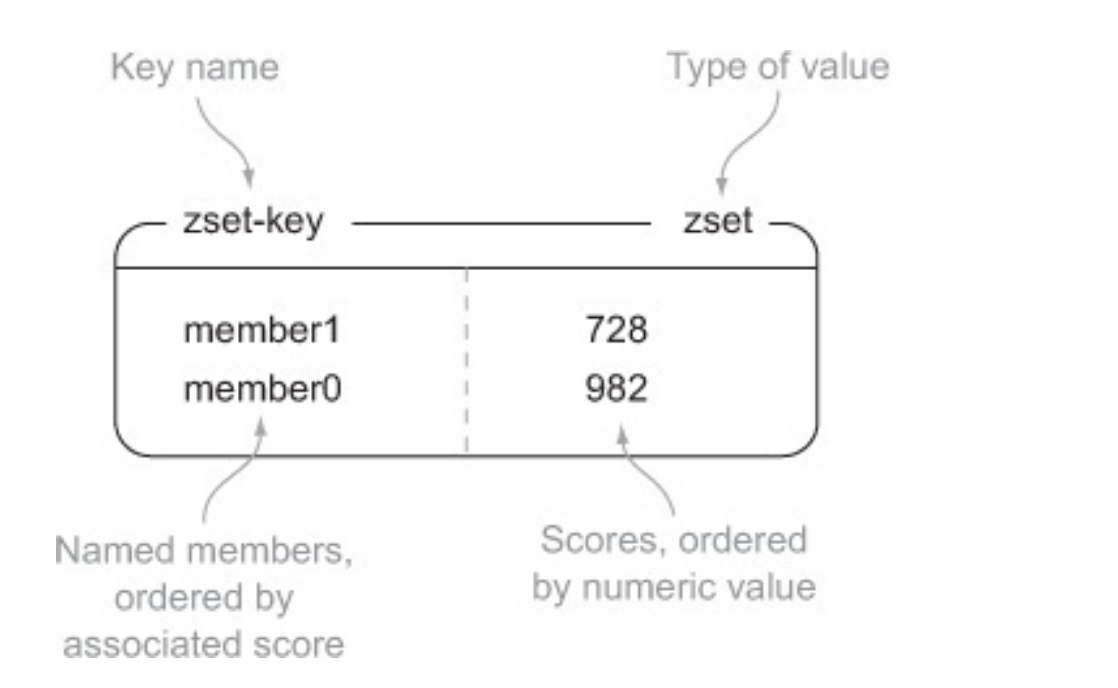
| Command | What it does |
|---|---|
| ZADD | Adds member with the given score to the ZSET |
| ZRANGE | Fetches the items in the ZSET from their positions in sorted order |
| ZRANGEBYSCORE | Fetches items in the ZSET based on a range of scores |
| ZREM | Removes the item from the ZSET, if it exists |
zrange zset-key 0 -1 withsocres
zrangebyscore zset-key 0 800 withscores
Redis expiration
There may, however, be cases where you’ve set a key but you know you will want to delete it after a certain amount of time has passed; in other words, you want the key to be volatile.
Setting Keys to Expire
set key_1 val_1 |
Other expiration cmd: - EXPIREAT (expire at Unix timestamp) - PEXPIRE (Time to live of the key is specified in milliseconds instead of seconds.) - PEXPIREAT (expire at Unix timestamp milliseconds)
Checking How Long Until a Key Expires
ttl key_1 // return time remaining until expiry (in seconds) |
The command returns -2 if the key does not exist.
The command returns -1 if the key exists but has no associated expire
Presisting keys
persist key_melon // clear timeout |
How Redis Expire Keys? 1
- Passive : A key is passively expired simply when some client tries to access it, and the key is found to be timed out.
- Actively (10 times per second): Continue to expire untile the percentage of keys that are likely to expire is under 25%
- Test 20 random keys from the set of keys with an associated expire.
- Delete all the keys found expired.
- If more than 25% of keys were expired, start again from step 1.
Redis Eviction
The eviction policy only applies to what happens when you exceed the max memory. As long as you're within your memory limits, volatile keys will expire when they should be expired.
maxmemory
Policies
noeviction
Don’t evict any data, returns error when memory limit is reached. Default
allkeys-lru
Evict any key, least recently used (LRU) first. Recommended.
allkeys-random
Evict keys in a random order.
volatile-lru
Evict keys with expiration only, least recently used (LRU) first.
volatile-random
Evict keys with expiration only in a random order.
volatile-ttl
Evict keys with expiration only, shortest time-to-live (TTL) first.
For LRU:
Not an exact LRU implementation
It will try to run an approximation of the LRU algorithm, by sampling a small number of keys, and evicting the one that is the best (with the oldest access time) among the sampled keys.
Tunning Configuration