LRU 算法学习
LRU
LRU - Least Recently Used (最近最少使用), 是一种缓存清除策略(cache eviction policy)
其他一些缓存清楚策略包含:
- FIFO(first in first out),队列的先进先出
- LFU (least frequently used), 优先清除访问次数最少的
- LRU(least recently used), 基于的假设是最近用到的数据后续被用到的概率也会很大
LRU 涉及到的操作
1. 读取
根据key来查询缓存获取对应的值, 读取时候还有同时需要相应操作维持最近使用情况
2.添加
第一个维度- 当前缓存是不是已经满了
会影响是不是需要进行删除操作
另一个维度 - 要添加的key是不是已经在缓存中
会影响是直接添加节点还是更新已有节点
LRU 涉及到数据结构
查询 - hashmap
插入,需要删除,移动 - Linked List , Doubly LinkedList (时间复杂度更小,鉴于删除时需要找到前驱节点,双向链表维护了前驱节点的指针)
哈希链表: hashmap + doubly Linked list
- hashmap 不需要存储value, 只存储key 并指向双向链表中对应的节点
- 双向链表存储K-V, 其实K也可以不用存,只存储value
代码实现
https://github.com/seashellzhb/LRU/blob/master/src/main/java/LRUCache.java
public class Node {
int key;
String val;
Node pre;
Node next;
public Node(int key, String val) {
this.key = key;
this.val = val;
}
}
|
public class DoublyLinkedList {
private Node head,tail;
private int size;
public DoublyLinkedList(){
head = new Node(0, "");
tail = new Node(0, "");
head.next = tail;
tail.pre = head;
size = 0;
}
public void addNodeLast(Node x) {
x.pre = tail.pre;
x.next = tail;
tail.pre.next = x;
tail.pre = x;
size++;
}
public Node removeFirst() {
if (head.next == tail) {
return null;
}
Node firstNode = head.next;
removeNode(firstNode);
size --;
return firstNode;
}
public int getSize() {
return size;
}
public void removeNode(Node node) {
node.pre.next = node.next;
node.next.pre = node.pre;
size --;
}
public void printDllNodes() {
if (head.next == tail ) {
System.out.println("Doubly linked list is empty");
return;
}
System.out.println("\n>>>>>>output start");
System.out.println("Total: " + size);
Node current = head.next;
while(current != tail) {
System.out.printf("%s:%s ", current.key ,current.val);
current = current.next;
}
System.out.println("\n<<<<<<output end\n");
}
}
|
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class LRUCache {
private Map<Integer, Node> map = new HashMap<>();
private DoublyLinkedList cache = new DoublyLinkedList();
public Map<Integer, Node> getMap() {
return map;
}
public DoublyLinkedList getCache() {
return cache;
}
public int getMaxCapacity() {
return maxCapacity;
}
private int maxCapacity;
public LRUCache(int maxCapacity) {
this.maxCapacity = maxCapacity;
}
public String get(int key) {
if (!map.containsKey(key)) {
return null;
}
adjustAsRecent(key);
return map.get(key).val;
}
public void put(int key, String val) {
if(map.containsKey(key)) {
deleteByKey(key);
addAsRecent(key, val);
}
if (maxCapacity == cache.getSize()) {
removeLeastRecent();
}
addAsRecent(key, val);
}
public void printCache() {
}
private void adjustAsRecent(int key) {
Node node = map.get(key);
cache.removeNode(node);
cache.addNodeLast(node);
}
private void deleteByKey(int key) {
Node node = map.get(key);
cache.removeNode(node);
map.remove(key);
}
private void addAsRecent(int key, String val) {
Node node = new Node(key, val);
map.put(key, node);
cache.addNodeLast(node);
}
private void removeLeastRecent() {
Node node = cache.removeFirst();
map.remove(node.key);
}
}
|
测试代码
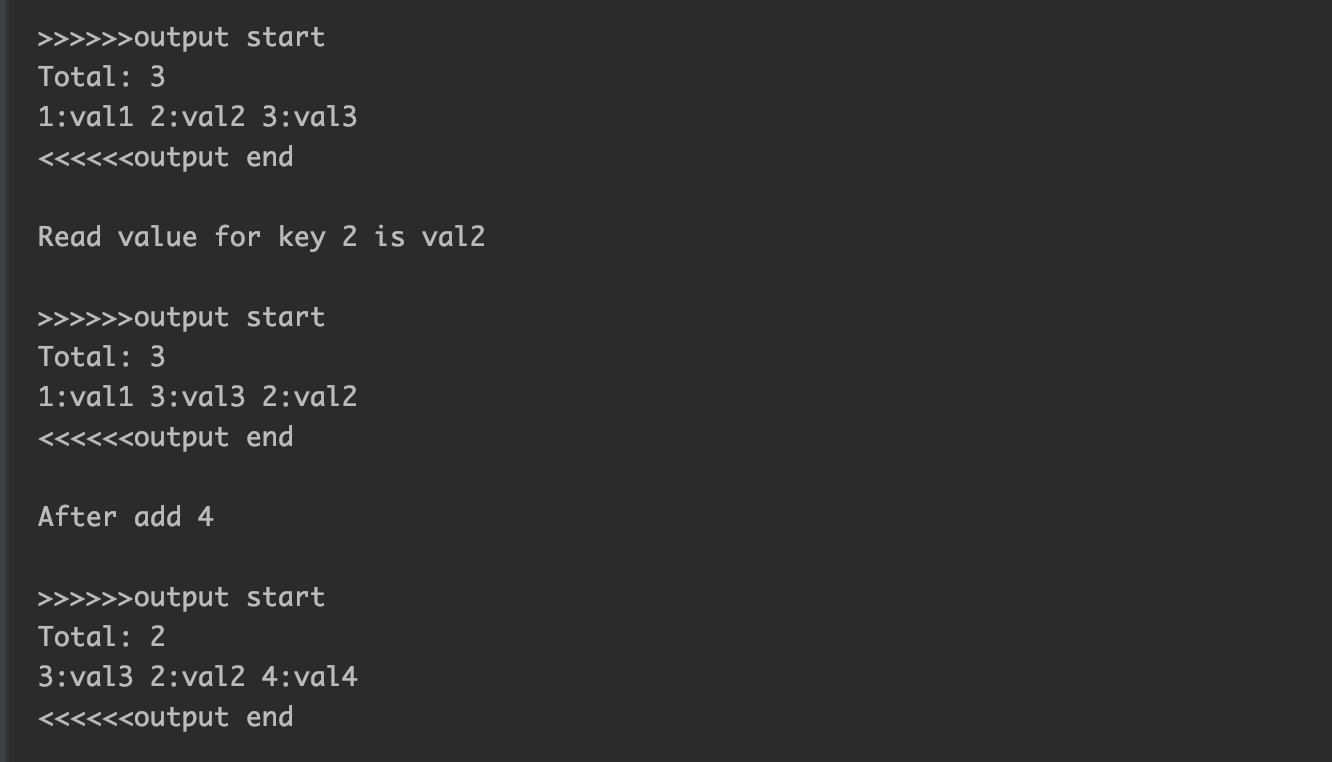
(简单起见,只是输出到stdout并没有assert verify)
import org.junit.Test;
public class LRUTest {
@Test
public void testLru() {
LRUCache lruCache = new LRUCache(3);
lruCache.put(1, "val1");
lruCache.put(2, "val2");
lruCache.put(3, "val3");
lruCache.getCache().printDllNodes();
String val_2 = lruCache.get(2);
System.out.printf("Read value for key 2 is %s %n", val_2);
lruCache.getCache().printDllNodes();
lruCache.put(4, "val4");
System.out.println("After add 4");
lruCache.getCache().printDllNodes();
}
}
|
console输出
参考
微信公众号-码农田小齐- 从 LRU Cache 带你看面试的本质
labuladong的算法小抄
