JMS学习笔记之MessageBasics
JMS学习笔记之MessageBasics
Message Basics
Heterogeneous integration is one primary area where messaging plays a key role.
fault tolerance
load balancing
scalability
transactional support for enterprises
Desitination
- queue
- topic
JMS is analogous to JDBC in that application developers reuse the same API to access many different systems.
Advantage of messaging
Heterogeneous Integration
Reduce System Bottlenecks
Increase Scalability
One way to increase the scalability of a system is to add multiple concurrent message listeners to the queue
Another way to increase the overall scalability of a system is to make as much of the system asynchronous as possible.
Increase End User Productivity
Architecture Flexibility and Agility
Centralized Architectures
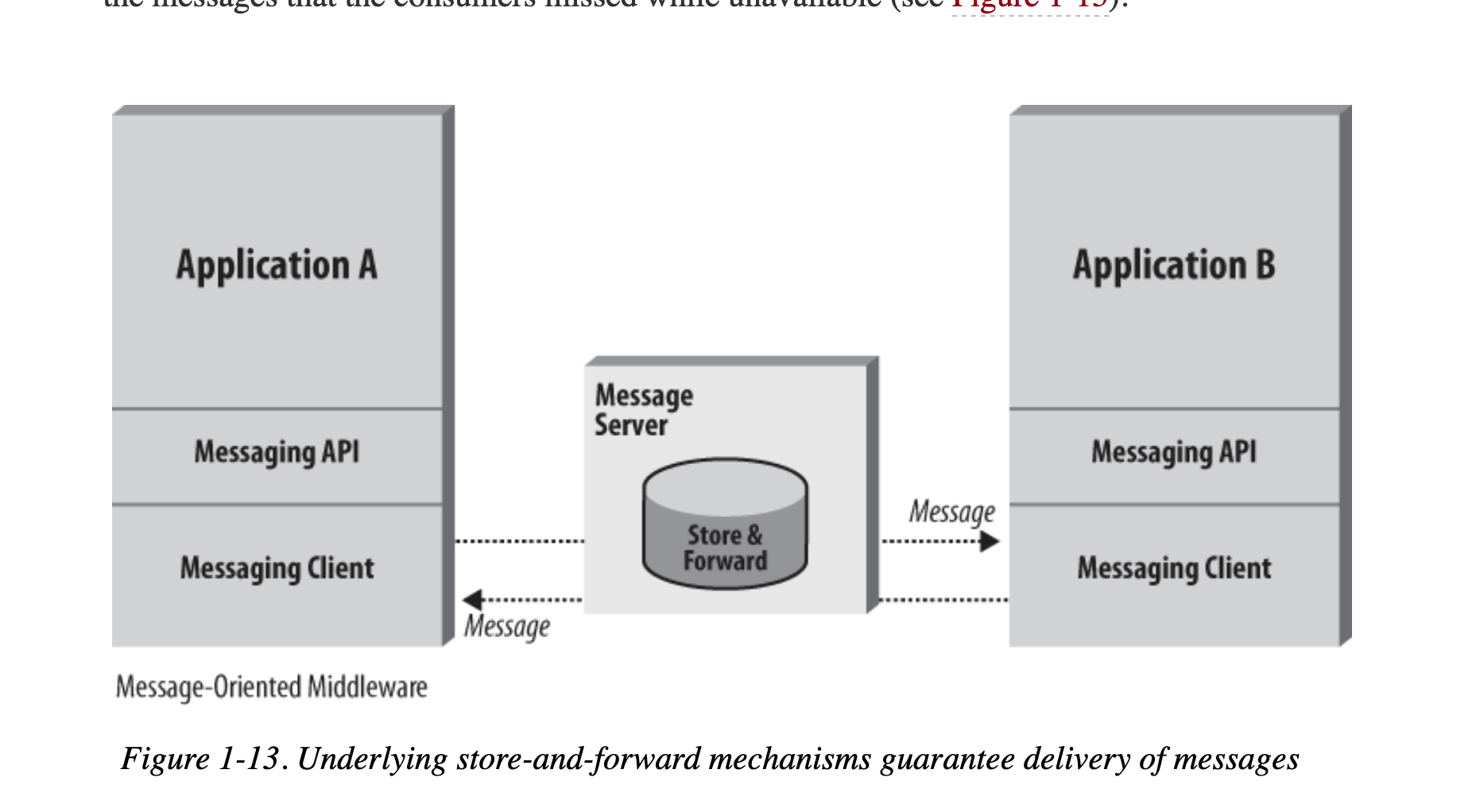
A message server, also called a message router or broker, is responsible for delivering messages from one messaging client to other messaging client
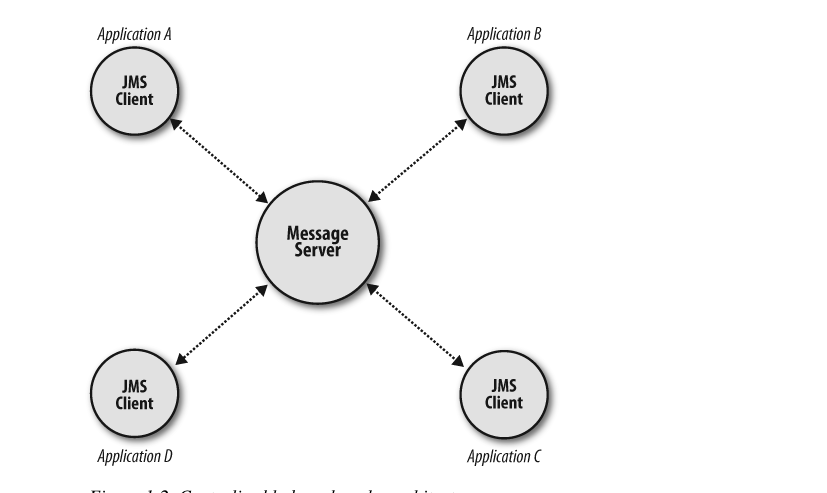
Decentralized Architectures
use IP multicast , no centralized server.
Messagin Model
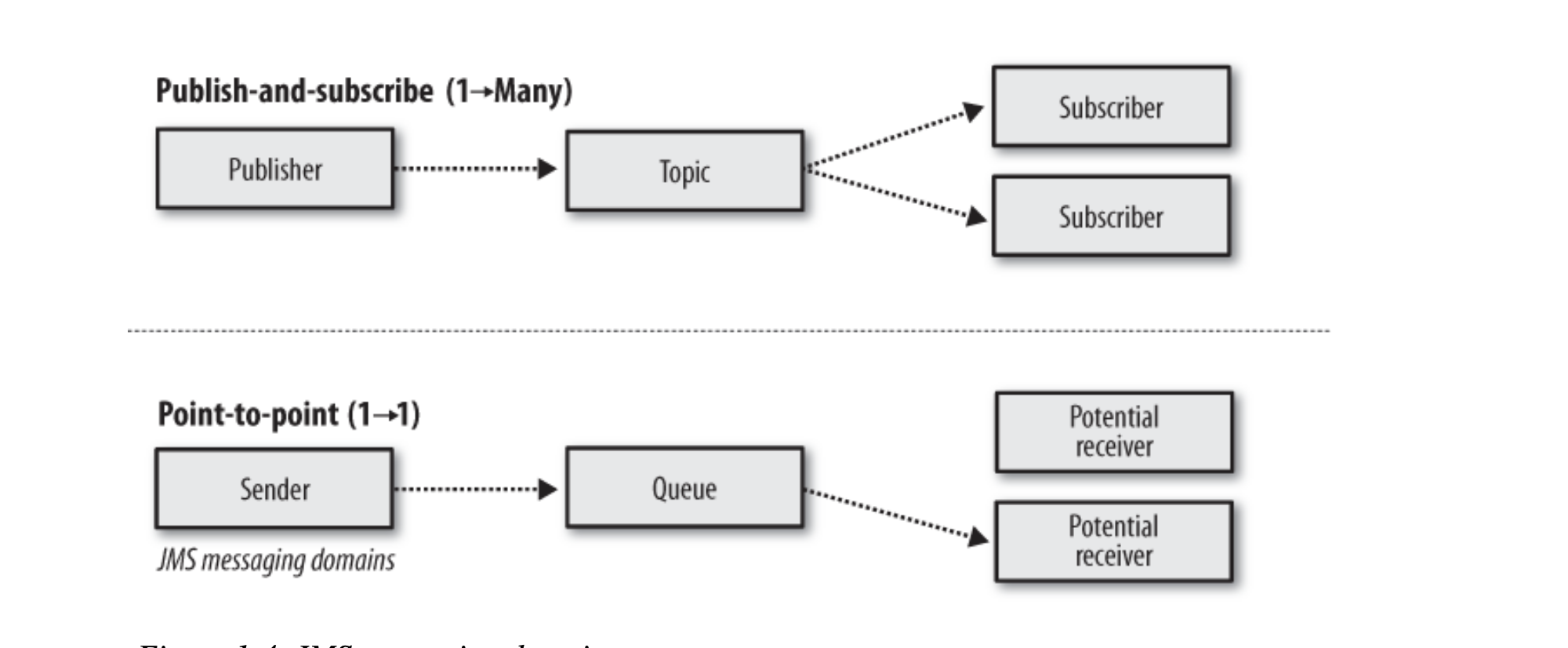
- point to point
- publish subscribe
A JMS application is a business system composed of many JMSclients and generally, one JMS provider.
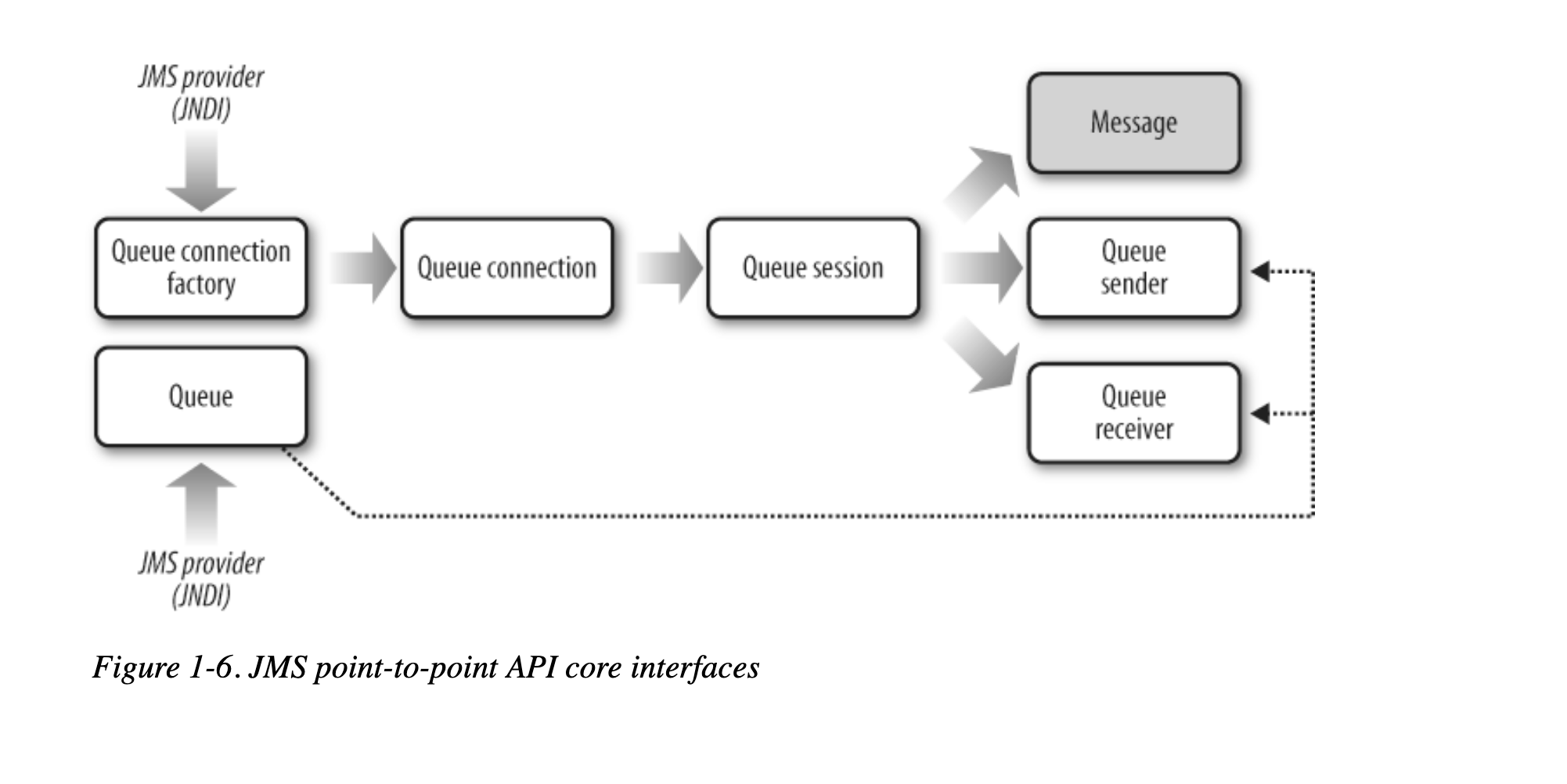
P2P
messages sent to a queue are received by one and only one receiver, even though there may be many receivers listening on a queue for the same message.
- (Async) fire and forget
- (Sync) request/reply
The point-to-point model supports load balancing, which allows multiple receivers to listen on the same queue, therefore distributing the load.
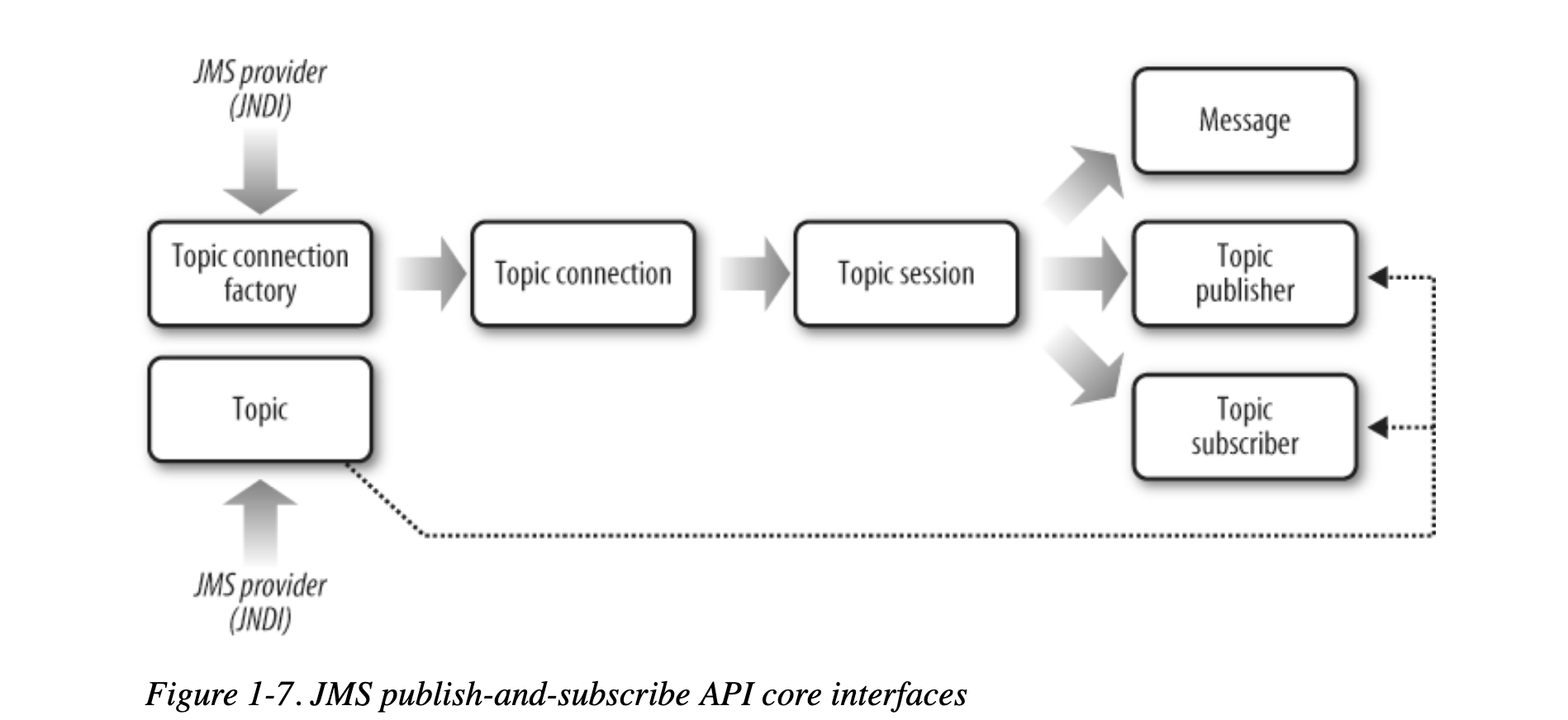
Pub/Sub
Every subscriber receives a copy of each message.
Subscribers:
- Nondurable: Receive messages only when they are actively listening on the topic
- Durable: will receive a copy of every message published, even if they are “offline” when the message is published.
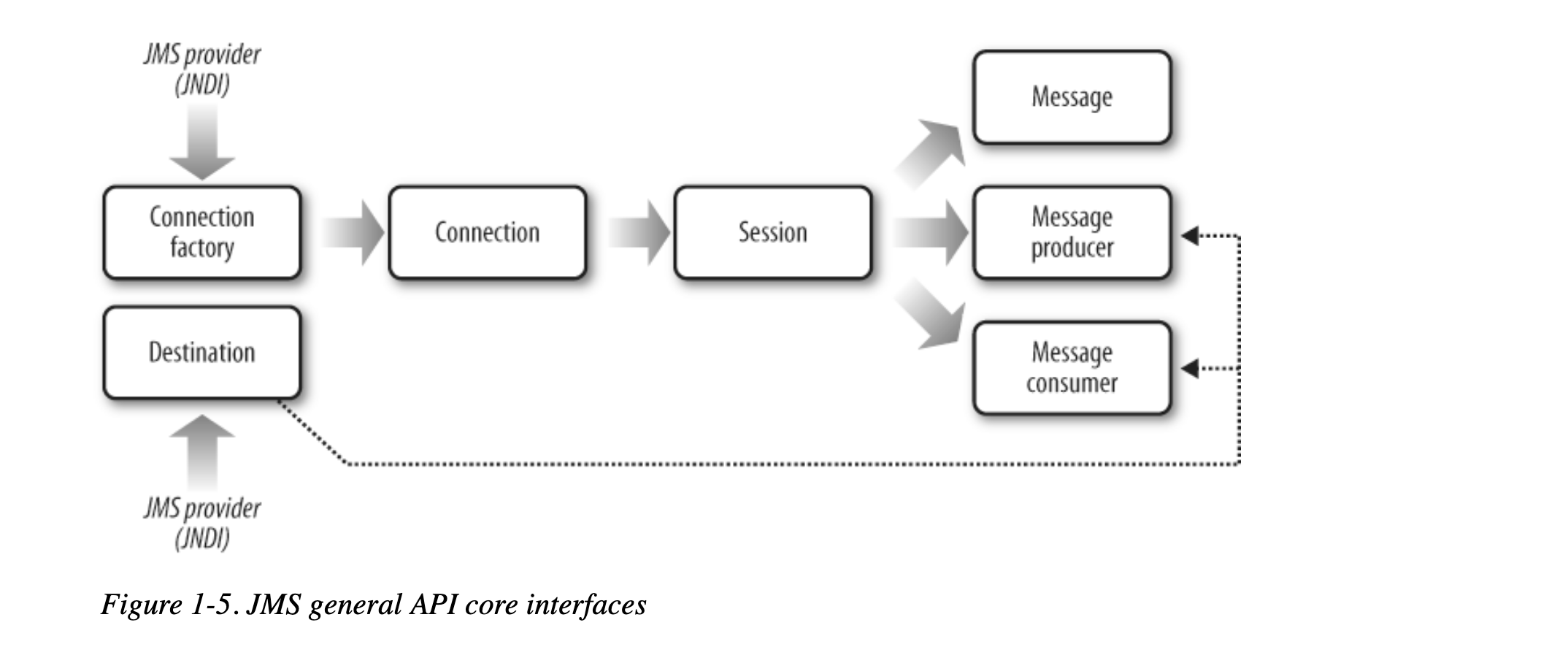
JMS API
- general API
- point to point API
- publish suscribe API
In general:
ConnectionFactoryDestinationConnectionSessionMessageMessageProducerMessageConsumer
the ConnectionFactory and Destination must be obtained from the provider using JNDI (per the JMS specification).
RPC vs Async Messaging
1. Tightly Coupled RPC
RPC attempts to mimic the behavior of a system that runs in one process. When a remote procedure is invoked, the caller is blocked until the procedure completes and returns control to the caller. This synchronized model allows the developer to view the system as if it runs in one process.
2. Enterprise Messaging
JMS provides guaranteed delivery - store-and-forward