前端- angularjs知识点
前端- angularjs知识点
Data Model Binding
one way
{{}}` same as ng-bind
`Hello {{name}}</span>
two way
ng-model bind
DI
Dependency Injection
Router
Frontend handle routing, key feature of SPA
Directive
manipulate dom - resuable
build-in directive
(ng-??)
- ng-repeat
- ng-model
- ng-bind
- Ng-show
- ng-class
- Etc...
bootstrap: ng-app, ng-controller, ng-module
Customize Directive
Check Directive secion
UT
jasmin + karma
Modules
Modules are AngularJS’s way of packaging relevant code under a single name
a module define its own controllers, service, factories and directives; module can depend on other modules as dependencies; module is the one bootstrap angualrjs: main entry point - passing module name to ng-app
define module :
angular.module('notesApp', []);
第二个参数是一个array - 这个module 所依赖的modules
Controller
angular.module('notesApp', []) |
Controller(): 第一个参数是contoller 名字,第二个参数是数组:数组最后一个是controller function, 前面是dependencies
notes: 以前用scope, angular 1.2 后controller as + this (this 最好assign给proxy variable)
eg
<html ng-app="notesApp"> |
Form
<form ng-submit="ctrl.submit1()"> |
valdiation
eg
<form ng-submit="ctrl.submit()" name="myForm"> |
| Form state | CSS class applied |
|---|---|
$invalid |
ng-invalid |
$valid |
ng-valid |
$pristine |
ng-pristine |
$dirty |
ng-dirty |
Other Form Controls
<textarea ng-model="ctrl.user.address" required></textarea> |
Services
AngularJS services are functions or objects that can hold behavior or state across our application.
Any service known to AngularJS (internal or our own) can be simply injected into any other service, directive, or controller by stating it as a dependency.
build-in services
AngularJS prefixes all the services that are provided by the AngularJS library with the $ sign
eg $log, $http, $window etc...
|
Creating services
- angular.module().factory
- factory return object contains service definition
- service act as application-level store which can hold state
Difference between factory, service and provider
Service can use javascript class
function ItemService() { |
Provider: can be useful when we need to set up some configuration for our service before our application loads.
$http
$http is a core AngularJS service that allows us to communicate with server endpoints using XHR.
.controller('MainCtrl', ['$http', function($http) { |
filter
AngularJS filters are used to process data and format values to present to the user
{{expression | filter}}
COMMON ANGULARJS FILTERS - currency - number - Lowercase/uppercase - json - etc...
filter filer: the filter filter in AngularJS is used to filter an array based on predicates or functions, and decide which elements of an array are included
Any filter, whether built-in or our own, can be injected into any service or controller by affixing the word “Filter” at the end of the name of the filter, and asking it to be injected
Eg : timeago
.filter('timeAgo', [function() { |
route
Any URL fragment after the # sign gets ignored by the browser in the server call.
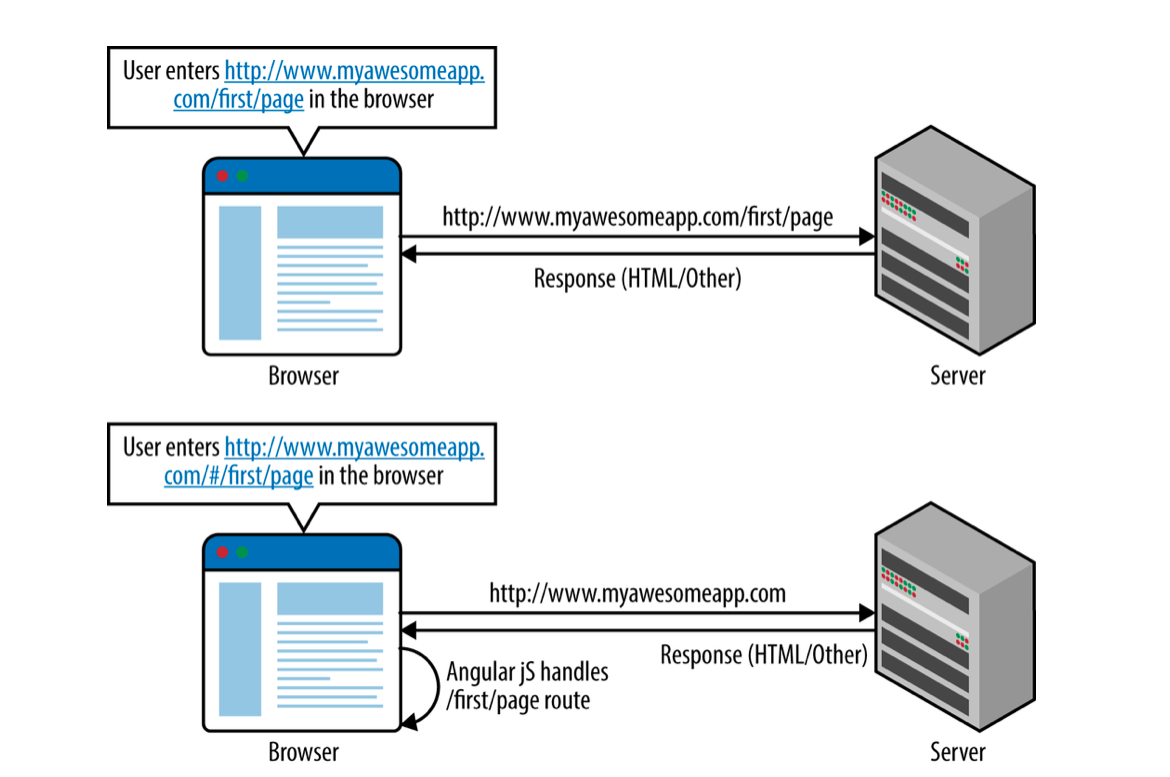
Angular ui-router
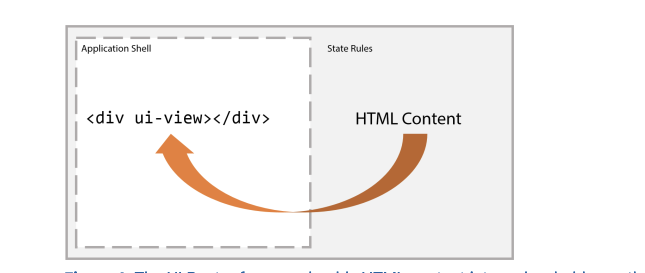
$stateProvider
- Call
$state.go(). High-level convenience method. Learn More - Click a link containing the
ui-srefdirective. Learn More - Navigate to the
urlassociated with the state. Learn More.
$stateProvider.state('contacts', { |
multi named view
<!-- index.html --> |
Directive
Behavior modifiers + Reusable components
retrcict: A(attribute), E(Element), C(class),M(comments)
link:it defines APIs and functions that are necessary for the directive, in addition to manipulating and working with the DOM
link: function($scope, $element, $attrs) {}
scope: By default, each directive inherits its parent’s scope, which is passed to link function.
- False: default, same as parent
- True, inherit while create a child scope of its own
- object: isolated scope, data need to be passed in through html attributes
- =: specifies that the value of the attribute in HTML is to be treated as a JSON object
- @: specifies that the value of the attribute in HTML is to be treated as a string,
- & sign specifies that the value of the attribute in HTML is a function in some controller whose reference needs to be available to the directive
replace
If we specify it to true, AngularJS removes the element that the directive is declared on, and replaces it with the HTML template from the directive definition object
complie
directive lifecycle: complie -> link
compile step in a directive is the correct place to do any sort of HTML template manipulation and DOM transformation.
Lifecycle
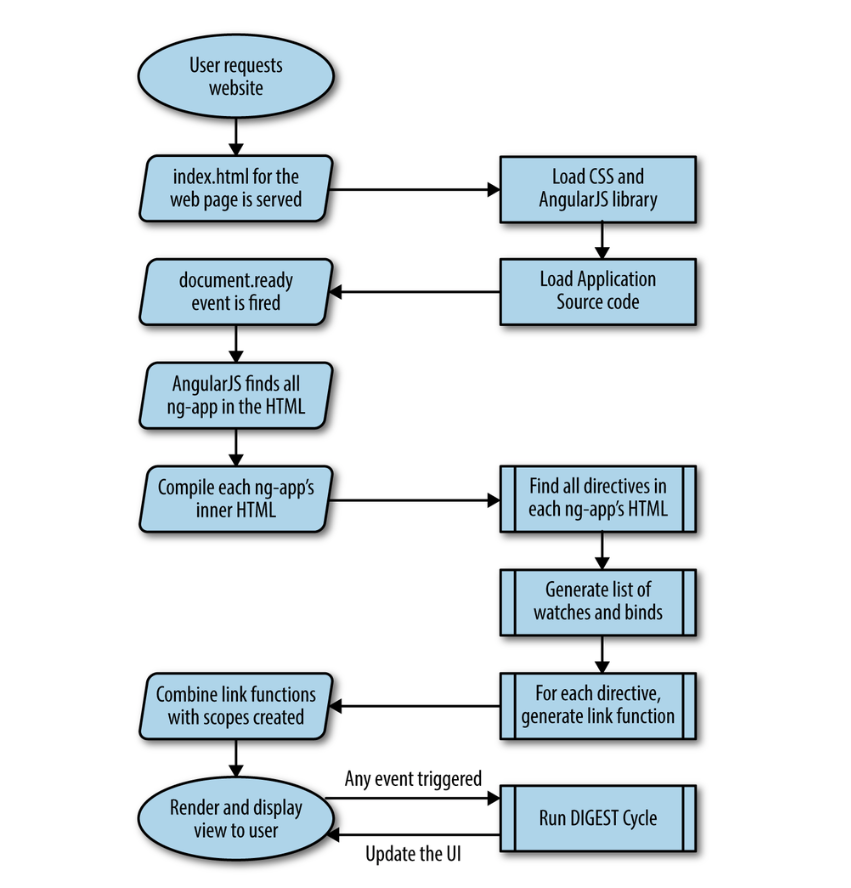
How angular detect changes and uddate UI?
Events:
- user make modification (types in , checks a checkbox, clicks a button)
- XHR
$timeoutor$interval
angular add watchers for all binding and ng-model, when above events happened, angularjs check if anything changed
The digest cycle
responsible for keeping the UI up to date in an AngularJS application. T
$rootScope.$apply function to ensure AngularJS knows to redraw the UI and run a complete digest cycle as needed.
$watch
get triggered by AngularJS whenever the variable under watch changes, and we get access to both the new and the old value in such a case.
Apply Vs Digest
主要是强制更新model,一般是outside angular(三方lib,原始生s)
https://www.tutlane.com/tutorial/angularjs/angularjs-watch-digest-and-apply-functions
broadcast vs emit + rootscope
http://www.binaryintellect.net/articles/5d8be0b6-e294-457e-82b0-ba7cc10cae0e.aspx
https://medium.com/@shihab1511/communication-between-controllers-in-angularjs-using-broadcast-emit-and-on-6f3ff2b0239d
$broadcast() as well as $emit() allow you to raise an event in your AngularJS application |
broadcast : 向下
emit: 向上
module dependencies
https://mobiarch.wordpress.com/2014/11/28/understanding-module-dependency-in-angularjs/
Use controller, directive and services from module dependency